Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that sensitizes the patient’s own immune system to fight against cancer. It boosts or alters how the immune system works, to improve, target or restore its function.
It has been found that though the body’s immune system is capable of killing cancerous cells, the cancer develops a mechanism to evade an immune response against it and this helps cancer continue to grow without being challenged by immune system.
The immunotherapy essentially focuses on breaking the cycle of immunity evasion by cancerous cells thus making them vulnerable to an attack by immune cells which helps us control cancer. Promising results have been obtained with few cancers and there is tremendous amount of research going on to expand its benefits for all cancer patients.
There are different kinds of immunotherapy that differ in the way that they elicit immune response against cancer. They have been approved for the treatment of several types of cancers including leukemia, lymphoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, melanoma and many others are being vigorously studied under clinical trials.
In this article we will try to help you understand the side effects caused by immunotherapy. These side effects primarily occur due to an activated immune system acting against cancer, that produces unwanted effects as well.
Side Effects: How do they develop?
Immunotherapy empowers the person’s immune system and enhances it to fight against cancer. However, it may not stop there all the time. Sometimes the immune system may become over-stimulated and that can affect the healthy cells and tissues in the body, leading to side effects.
The side effects of immunotherapy are different from those which are related to conventional cancer treatments. They also differ depending on the type of immunotherapy and the specific cells that are affected by the same, dose, location, stage of cancer, and general health of the patient.
They may range from mild to moderate in severity and are reversible if detected early and addressed appropriately. Many of them can be managed with medicines such as steroid medications. Sometimes they can also increase the patient’s risk for autoimmune disorders or other life-threatening complications.
Hence, patient education related to possible symptoms that may occur during, or after, the treatment with immunotherapy, and an emphasis on seeking medical care right away when any unusual symptom is noticed is of paramount importance.

Common side effects of immunotherapy
1. Skin and mucosa side effects
Localized or generalized skin related side effects are more common with immunotherapy. Rashes and itching are common skin related side effects. They can be mild with minimal symptoms, or severe, affecting the patient’s ability to take care of themselves.
Rarely, skin problems associated with other complications like infections could turn severe and require hospital admission. Other problems include hair loss, loss of skin pigmentation, itchy lesions, fluid filled blisters, dry skin and even mouth sores, make it difficult to drink or eat. Hair loss may occur as round patches on the scalp that may eventually lead to complete loss of hair on the body.
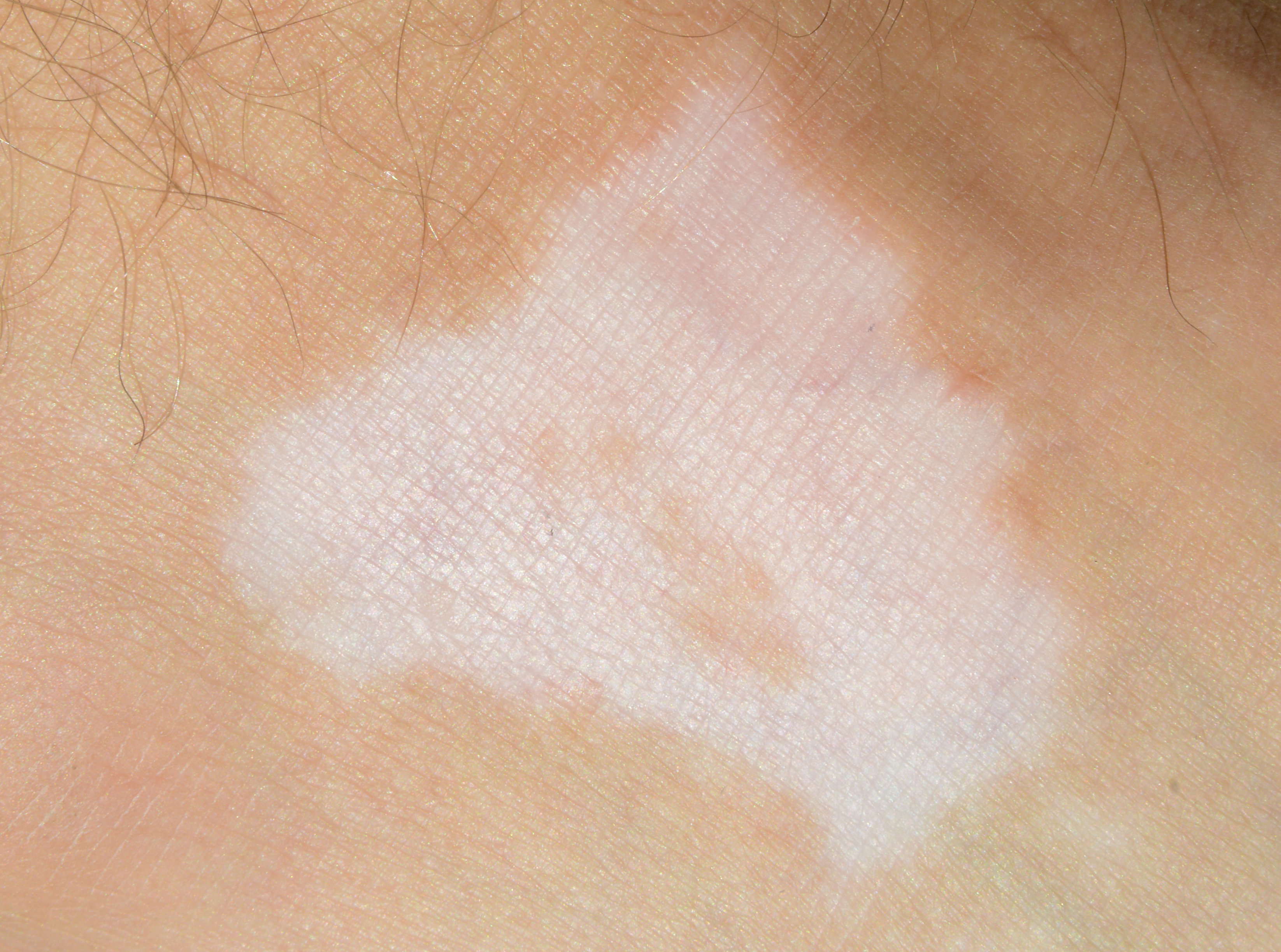
At times, the skin may turn sensitive to sunlight and the skin on the fingertips may become swollen and cracked. Rarely, firm bumps known as granulomas may occur.
Management
Avoid anything harsh on the skin. Use mild, fragrance-free soaps and lukewarm water for bathing. Moisturize the skin with the help of a good and unscented cream, to soothe it and keep it well-hydrated. Avoid sun exposure, and use a sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher while going out. If the symptoms persist, consult a dermatologist to prevent any serious complications.
2. Fatigue
Like with other cancer treatments, fatigue is a common side effect for immunotherapy as well.
Oversleeping, difficulty in remembering things, decreased work efficiency, spending less time with family and friends are some indicators of fatigue. Monitoring for patient’s fatigue levels throughout the treatment and during recovery is important.

Management
Plan your daily activities at a time when you feel more energetic during the day and ensure that you get enough rest. However, excessive sleeping during the day may make one feel more tired. Limit day time naps to less than one hour. Drink at least eight glasses of water per day and stay hydrated. A short walk or light exercise may help you feel energized.
3. Flu-like symptoms
Flu-like symptoms typically occur in non-specific immunotherapy treatment like interferons and interleukins, and oncolytic virus therapy. Common flu-like symptoms include headache, sinus congestion, nausea, dizziness, muscle or joint aches, chills, weakness, and fluctuations in blood pressure.

Management
Flu-like side effects usually subside naturally without any treatment. Staying hydrated is important, sipping water or juice throughout the day helps to stay away from dehydration. OTC medications may sometimes help to relieve pain with doctors’ advice.
4. Diarrhoea
Gastrointestinal toxicity in the form of diarrhoea is one of the most common side effects caused by immunotherapy, especially with checkpoint inhibitors. It may vary in severity and the associated symptoms may include stomach cramping, blood in stool, nausea, dehydration, fever or rapid heart rate. Excessive diarrhoea may lead to severe dehydration that could be fatal. One should be informed about the relative side effects and its complications.

Management
Stay hydrated by drinking water or clear liquids throughout the day. Avoid foods that may irritate the stomach and worsen diarrhoea, such as milk or milk products or fiber rich foods. Eat frequent small meals and include mild foods that are easy to digest. Take probiotics, anti-diarrheal or corticosteroids in case of severe diarrhoea.
Other possible side effects of immunotherapy may include:
- Neurological symptoms manifested as breathing difficulties, muscle weakness or numbness.
- Rheumatological symptoms such as mild to moderate muscle or joint pain.
- Cardiac symptoms related to heart muscle inflammation, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or irregular heartbeat
- Kidney symptoms related to impairment of kidney function, such as swelling in legs, fatigue, persistent nausea, or unexplained weight loss.



