The term “robotic” often misleads people. Robots don’t perform surgery. It is the surgeon who performs surgery using a computer-controlled robot.
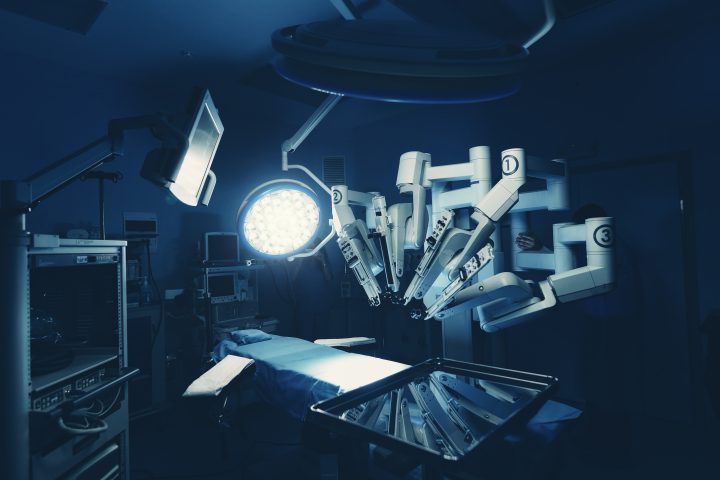 Usually, surgeons make large incisions in skin and muscle so that they could directly see and work on the area of concern. This is called open surgery. Today many surgeries can be performed using minimally invasive laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery.
Usually, surgeons make large incisions in skin and muscle so that they could directly see and work on the area of concern. This is called open surgery. Today many surgeries can be performed using minimally invasive laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery.
Both minimally invasive surgical options require a few small incisions that cancer doctors use to insert surgical equipment and a camera for viewing. In laparoscopic surgery, doctors use special long-handled tools to perform surgery while viewing magnified images from the laparoscope (camera) on a video screen.
Robotic surgery is an advanced form of minimally invasive surgery where the surgeon sits on a console or computer outside the operation theatre and performs surgery with the help of a computer-controlled robot.
In the past two decades, robotic surgery has made a paradigm shift in surgical practice. Currently, the Da Vinci Surgical System is the only FDA approved and commercially available robot in the world. Its Xi, fourth generation surgical system, is in trend and this system is an assembly of :
-
Surgeon Console
The surgeon sits here and controls the instruments while viewing anatomy in high definition 3D.

-
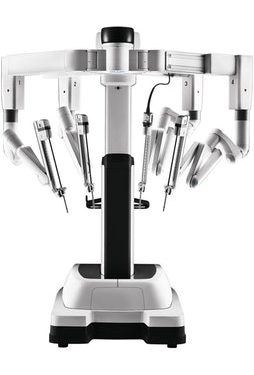
Patient Cart
It is positioned along-side OT table in Operation theatre. The patient cart holds the camera and instruments that the surgeon controls from the console.
-
Vision Cart
The vision cart makes communication between components possible and supports the 3D high definition vision system.

Robotic Surgery: What to expect?
While each surgery is different, here are the general steps to a Robotic-assisted surgery:
- The surgeon makes tiny (one to two centimetre-long) incisions in the body.
- The surgeon inserts a miniature robotic instrument and a powerful camera into the body.
- The surgeon then sits at a nearby console (a large computer) to direct the procedure. At the console, the area of operation can be seen highly magnified, with excellent resolution.
- Sitting at the console, the surgeon manipulates the controls.
- The instruments respond to these movements and translate them into precise, real-time movements inside your body.
- The robotic devices, which have greater dexterity and range of motion than a human, allow the surgeon to successfully perform delicate surgeries in hard-to-reach places.
Robotic surgery for cancer treatment
Robotic Surgery has become a new standard of treatment for many cancers including Urological, gynaecological, colorectal and trans oral surgeries. These particular organ-based surgeries have also got FDA approvals. After its successful recognition in the above mentioned areas, the robotic surgery is now being appreciated in Upper GI and thoracic as well.
Minimally invasive approach in oncological surgery is usually inspired by its improving perioperative outcomes, functional results, minimal complications, and uncompromised oncological principles. A survey of members of the Society of Gynecologic Oncologists found that 97% of respondents reported using the robot in 2012, compared with only 29% in 2007.
There was a significant increase in the perceived appropriateness of robotic surgery for a radical hysterectomy and lymph node dissection for the management of cervical cancer over time, from 60.2% in 2007 to 89.1% in 2012. The robot was favoured over traditional laparoscopy for cervical cancer in 75% of respondents by 2012.
Commonly performed Robotic Surgeries:
- Radical prostatectomy
- Robotic radical nephrectomy
- Colorectal Surgery (Total Mesorectal excision, TME)
- Trans oral robotic surgery (TORS)
- Radical Hysterectomy and other gynaecological procedures
Potential benefits of robotic surgery for patients include
- Reduced pain
- Lower risk of infection or complications
- Less blood loss (fewer transfusions)
- Shorter hospital stays
- Better cosmosis
- Faster return to normal activities (e.g., sexual function, urinary continence)
- Improved quality of life
Limitations of robotic surgery
- Expensive – The high cost of installing a robotic surgery system can increase the cost of a surgical procedure. Surgical robots are costly to maintain, and their operation requires additional training, which is also expensive
- Requires expertise
- Mechanical failure – a chance of breakdown
Dr. Ashutosh Mishra is Senior Surgical Oncologist at VPS Rockland Hospital in Delhi. An alumnus of All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), he has more than 12 years of surgical experience, with expertise in gastrointestinal, genitourinary and gynaecological oncology. He is also an expert in cytoreductive surgeries and HIPEC.


