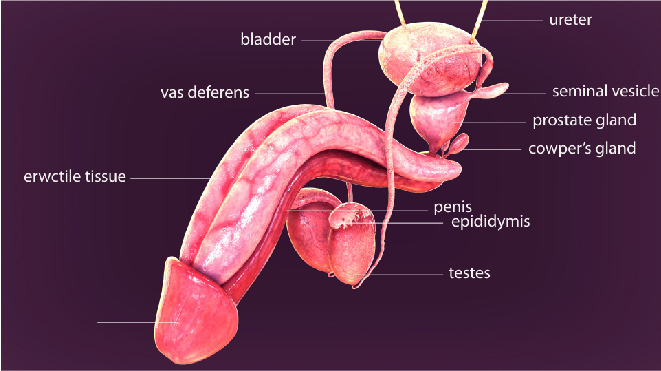
Testicular cancer is the cancer in the testicles, the male reproductive organ that makes hormones and sperm. To learn more about testicular cancer, read here. Surgery is the first option of treatment recommended for all cases of testicular cancer, since in all the stages the one or both testicles have to removed.
How surgery works in eliminating cancer:
Surgical procedures are used to remove the tumours. This procedure is carried out by the doctor making small cuts into the abdomen above the pubic area and removing the testicle along with the spermatic cord. Surgical procedures need a lot preparation and after care, which means that the pre and post surgery are also important phases. General procedure of surgeries for treating testicular cancer:
Before surgery: The patients are taken into the operation theatre and made to lie down on a table. They are often given local anesthesia in the groin area to numb the pain. Sometimes, the patient is made to sleep by giving anesthesia to the entire body.
During surgery: Depending on the type of surgery, the procedure is carried out. For testicular cancer, testicle removal is the aim.
After surgery: Post surgery, the patient is sent to a recovery room, where he is monitored for 1-2 days.
Types of surgery:
Depending on the diagnostic results of the patient, the doctor will decide the best surgical procedure for patients. Know about the diagnostic tests are performed here. Following are the surgical procedure used for treating testicular cancer:
Radical inguinal orchiectomy
This is one of the most recommended surgeries for treating testicular cancers. Almost all types of treatments start with a surgery to remove the testicles with cancer. And this surgery is known as radical inguinal orchiectomy. In most of the cases, only one testicle is removed as it is very rare that both the testicles develop cancer and have to be removed. The procedure of removing both the testicles is known as bilateral orchiectomy.
The surgery involves making an incision along the beltline in the groin and completely removing the testicles along with the spermatic cord. The spermatic cord contains the blood vessels, which is why it is removed as it could behave as a pathway to spread the cancer.
Orchiectomy is used in diagnosing and treating all stages of seminomas and nonseminoma too. The radical inguinal orchiectomy might be delayed to be performed after chemotherapy for advanced stages of testicular cancer. Before the surgery, blood samples of the patient are collected for tumour marker tests. These results help in planning the treatment and follow up.
Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND):
This procedure is used to remove the retroperitoneal lymph nodes that are present in the back of the abdomen. RPLND is a very complex surgery and is to be done only by highly experienced surgeons. The procedure involved making an incision in the middle of the abdomen. This treatment is very beneficial in restricting the growth of the cancer as it removes the lymph nodes.
Laparoscopic RPLND is a new procedure, in which smaller incisions are made to remove the lymph nodes. This surely has fewer side effects than the regular open RPLND. But it’s effectiveness is still being studied, and hence is not completely in practice.
RPLND is also used for removing the residual tumours post chemotherapy.
What complications could arise due to surgical procedures?
Any surgery will have complications post treatment. But these vary depending upon the area which has been surgically treated, patient’s general health, type of surgery and most importantly stage and type of cancer. Following are the common side complications that arise after surgical procedures for testicular cancer:
- Hematoma (bleeding into the scrotum)
- Swelling and pain of scrotum
- Bowel obstructions
- Depression
- Mood swings
- Fatigue
- Lowered testosterone level
- Removal of both testicles can result in lower sex drive
- RPLND can cause damage to the nerves that are responsible for ejaculation.
- Retrograde ejaculation, a condition where the semen does not escape out from the urethra but goes backwards into the bladder.
Not every patient has all the same complications, they can differ in each patient. In case of any of the mentioned complications, a doctor is to be consulted immediately. Patients will be able to cope up with the side effects by having proper follow up.
Outlook:
Surgical treatments are successful in removing the tumours/testicles. Surgeries to remove testicular cancer are also used to restrict the growth of the cancer by RPLND.
Orchiectomy has a good success rate in eliminating cancer. In patients who have one to five lymph nodes affected, RPLND has 80-90% success rate in eliminating the cancer. The remaining 10-20% men have a recurrent testicular cancer. For patients who have more than 5 lymph nodes, the success rate of RPLND is about 50%.
After care:
Post surgery, the patients will have to take utmost care in order to avoid recurrence of cancer and to cope up with its complications. Read more the follow up care for testicular cancers here. Following a few tips which help the patients take proper care of themselves:
- Not too much of physical activity for two to four weeks after surgery
- Wear loose pants
- Take advices from a nutritionist about your food
- Manage long term side effects but taking regular health check-ups
- Consulting a doctor on noticing any complications
- Frequent blood cell monitoring is recommended
- Constantly monitor for recurrence and in case the cancer has recurred, immediate treatment has to be taken
- Maintain personal health records