Cancer is a multifaceted disease that can be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some people may have a higher risk of developing cancer due to their genetic makeup, which may be passed down from their parents. We call it inherited cancer or hereditary cancer. Not all cancers are hereditary, some may occur due to a combination of genetic mutations, and environmental and lifestyle factors of an individual that happen during one’s lifetime. Such type of cancer is referred to as sporadic cancer and the risk of developing sporadic cancer increases with age. This blog provides insights into the risk of inheriting cancer and measures that can be taken to prevent it.
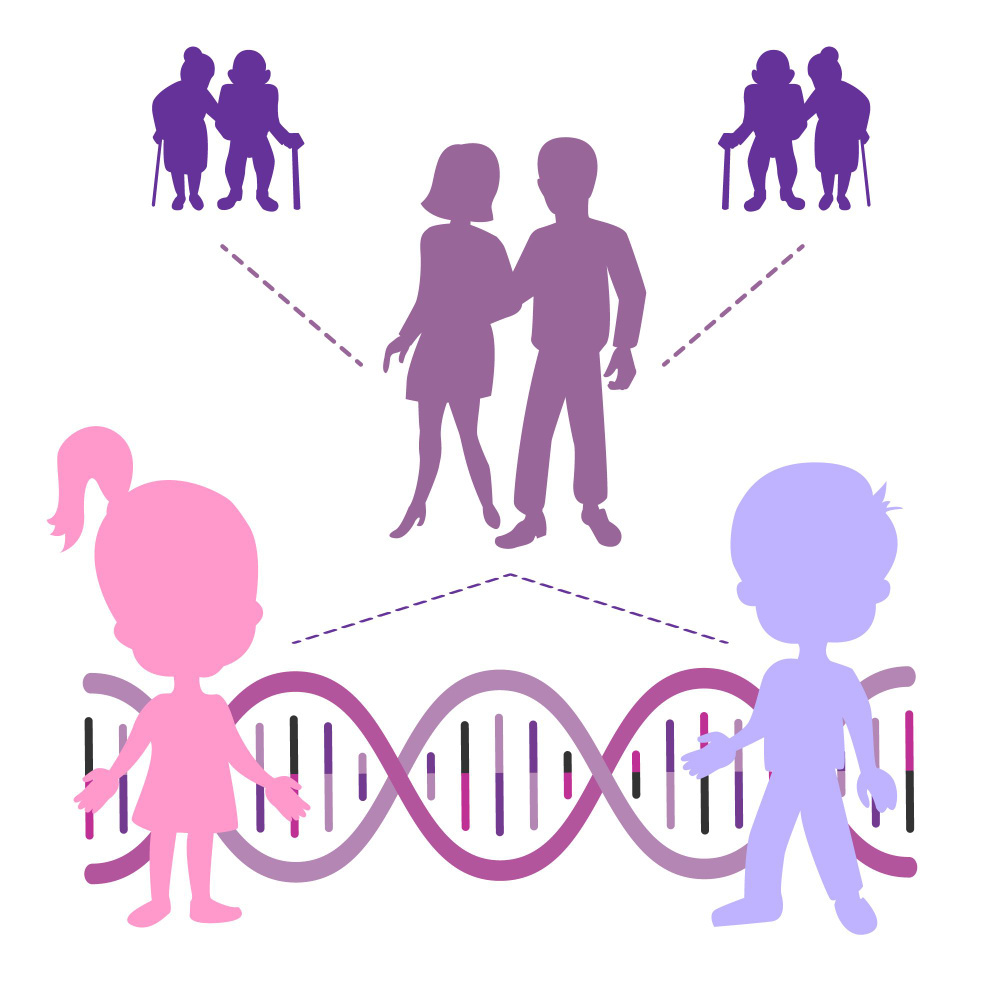
Inherited cancer and sporadic cancer are different forms of cancer that differ in their development process.
Inherited cancer, also known as hereditary cancer, is caused by genetic mutations passed from parents to their children. People who inherit these mutations are more likely to develop certain types of cancers at a younger age than people without the inherited mutations. Inherited cancers account for about 5-10% of all cancer cases.
On the other hand, sporadic cancer is caused by genetic mutations that occur during a person’s lifetime due to exposure to environmental factors such as tobacco smoke, UV radiation, and certain carcinogenic chemicals, as well as individual factors such as ageing and certain medical conditions. Sporadic cancers are more common in today’s lifestyle, accounting for 90-95% of all cancer cases.
Know About Carcinogens & Safeguard Against Their Harmful Effects
The key difference between inherited and sporadic cancer is the origin of the genetic mutations that lead to cancer. Inherited cancer is caused by genetic mutations that a person inherits from their parents at birth, while sporadic cancer is caused by genetic mutations that occur during a person’s lifetime.
Even though sporadic cancer occurs randomly without a known genetic cause, there are still ways to reduce the risk of developing cancer. Lifestyle factors such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, and protecting yourself from sun exposure can all help reduce the risk of developing cancer. Additionally, regular cancer screenings can help detect cancer early when it’s most treatable.
If cancer has affected your family for several generations, or if your family has multiple cases of the same cancer type or more than one type of cancer in a single person, you should consider it as a risk factor for inheriting cancer.
There are several ways to determine if you have a genetic predisposition to cancer. One option is to undergo genetic testing, which identifies specific gene mutations that increase the risk of developing cancer. Another option is genetic counselling. If you are concerned about your risk of inheriting cancer, the best way to determine your risk is to consult a doctor and/or a genetic counsellor. This can also help you understand your risk and develop a plan for prevention.
Your doctor evaluates your personal and family medical history to estimate your risk of developing certain types of cancer. Your doctor may also perform a physical exam and recommend additional tests or screenings, such as blood tests or imaging scans to inspect your risk.
A genetic counsellor can also help you understand your risk of inheriting cancer. They can review your family medical history and assess the likelihood of a genetic mutation being present in your family. They can also explain genetic testing options, help you interpret the results, and provide recommendations for managing your risk.
Genetic testing can help detect certain gene mutations that increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer. Genetic testing can be especially helpful for individuals with a family history of cancer, as certain gene mutations can be inherited from parents. A genetic counsellor can provide guidance on whether genetic testing is appropriate for you and can help interpret the results of the test.
Genetic testing can be a complex process, so it is important to have it done by a specially qualified healthcare professional.
If you have a genetic predisposition to cancer, there are several steps you can take to reduce/prevent your risk. Some of these steps include:
Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is an important way to reduce your risk of developing cancer. This mainly includes exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption.
Regular screening: Regular cancer screenings can help detect cancer early when it is most treatable. The type of screening test a person should undergo will vary depending on their age, sex, risk factors, personal or family medical history, and several other factors. For example, women with a high risk of breast cancer may be recommended to undergo regular mammograms and breast MRI screenings.
Prophylactic surgery: In some cases, prophylactic surgery may be recommended to remove tissues or organs that are at high risk of developing cancer. For example, individuals with a high risk of ovarian cancer may choose to undergo prophylactic removal of their ovaries and fallopian tubes. While this option may not be appropriate for everyone, it can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer.
Chemoprevention: Chemoprevention involves taking medications to reduce the risk of developing cancer. This may be an option for individuals with a high risk of certain types of cancer. For example, tamoxifen is a medication that can reduce the risk of breast cancer in women with a high risk of developing the disease.
The majority of cancers are not inherited and are instead caused by a combination of environmental, lifestyle, and other factors. However, the most common types of cancers that can be inherited genetically are:
Breast cancer: Genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, significantly increase the risk of developing breast and ovarian cancers.
Colorectal cancer: Lynch syndrome is an inherited genetic condition that increases the risk of developing colorectal cancer and other types of cancer, such as endometrial, ovarian, stomach, pancreatic, and urinary tract cancers.
Melanoma: Mutations in genes such as CDKN2A and CDK4 can increase the risk of developing melanoma, a type of skin cancer.
Pancreatic cancer: Some inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA2, PALB2, and STK11, increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
Ovarian cancer: Inheriting mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes increases the risk of developing ovarian cancer.
It’s important to note that not all cancers are hereditary, and having a family history of cancer does not necessarily mean you will develop the disease. However, people can be at risk of inheriting certain types of cancers if they have a family history of the disease. To understand your risk, talk to a doctor and make informed decisions about your health and take the necessary steps to prevent or detect cancer early. You can reduce your risk of inheriting cancer by following a healthy lifestyle and staying away from cancer-causing environmental or lifestyle factors. It is also recommended to get the screening tests under your doctor’s guidance.
Related Articles:
Can Women Really “Inherit” Ovarian Cancer?
15 Tools to Keep Yourself Healthy
కీమోథెరపీ కోసం క్యాన్సర్ రోగులు ఎలాంటి దుస్తులు ధరించాలో తెలుసా? ఈ ఆర్టికల్లో, క్యాన్సర్ రోగులకు కీమోథెరపీని సౌకర్యవంతంగా పొందడంలో సహాయపడే దుస్తుల జాబితాను అందించాము.
ఈ కథనం మీ క్యాన్సర్ రకానికి సరైన క్యాన్సర్ వైద్యుడిని కనుగొనడానికి 6-దశల గైడ్ను వివరిస్తుంది.
तंबाकू का सेवन गुटका, जर्दा, पैन मसाला आदि के रूप में करना सिर और गले के कैंसर का मुख्य कारण…
నోటి పుండ్లతో బాధపడుతున్న క్యాన్సర్ రోగులకు క్యాన్సర్ చికిత్సలో ఉన్నప్పుడు తీసుకోవాల్సిన 12 ఉత్తమ ఆహారాలు.
క్యాన్సర్కు కారణమయ్యే 6 జీవనశైలి కారకాలు గురించి ఈ కథనంలో వివరంగా ఇవ్వబడ్డాయి. అవి ఏమిటో తెలుసుకోండి!
शोध की मानें तो न्यूज़पेपर प्रिंट करने में जो स्याही का इस्तेमाल होता है उसमें ऐसे केमिकल होते हैं जो…