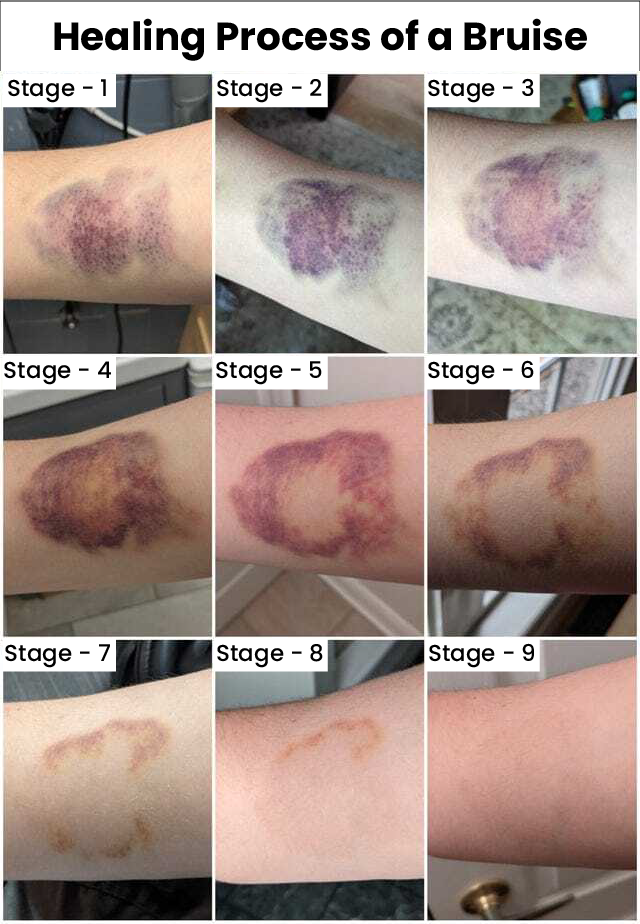
Bleeding and bruising are side effects that may occur due to cancer treatments. Bleeding is the release of blood either outside the body or into a body cavity due to a broken blood vessel. Bruising is bleeding into the skin from damaged blood vessels due to trauma. Bruising often causes the appearance of black and blue coloured spots on the skin.
Why Do Patients Bleed And Bruise During Cancer Treatment?
Mostly, patients under cancer treatment will bleed and bruise due to low platelet count (also known as thrombocytopenia). Because platelets are the key to clot blood to stop bleeding. Other reasons for bleeding and bruising are liver problems, low vitamin K, or weak blood vessels. To treat thrombocytopenia, Your treating team will suggest platelet transfusion or prescribe medicines that stimulate the production of blood cells in the body.
Here Are Some Reasons For Bleeding And Bruising In Cancer Patients;
Cancer patients may experience bleeding and bruising due to any of the following:
Certain Cancers:
Blood cancers (Leukemia and lymphoma), cancers that have spread to the liver, cancers of the spleen that makes the spleen bigger to hold platelets in it without circulating throughout the body, and cancers that have spread to bone marrow. All these cancers reduce the platelet count in the body and make the cancer patient face bleeding and bruising.
Cancer Treatments:
Not all cancer treatments cause bleeding and bruising. It depends upon treatment type and dose, medicines used, or site of treatment.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may cause a decrease in the production of blood cells from bone marrow. This may result in a low platelet count.
Click here to know Why Does Blood Cell Count Fall During Chemotherapy
Radiation Therapy: Bleeding and bruising are not side effects of all radiation treatments. But if radiotherapy is given along with chemotherapy or if you are receiving larger amounts of radiotherapy to the pelvic region, it decreases the platelet count.
Surgery: If you have undergone surgery for the removal of tumours, then bleeding and bruising happens as the most common side effects. You can observe the leaking of blood through the surgery site. If this condition worsens or the bleeding persists, inform your treating team and get immediate medical care.
Certain Medications:
Medicines like blood thinners (Heparin, Warfarin, etc) and NSAIDs (Aspirin, Ibuprofen, etc) increase the risk of bleeding. Ask your health care team to provide a list of medications to avoid during cancer treatment to prevent bleeding and bruising.
Antibodies: Antibodies are used to kill viruses and bacteria, but sometimes they are also involved in destroying healthy platelets resulting in low platelet count. So, ask your doctor before taking any vaccination.
What Are The Symptoms Of Bleeding And Bruising?
There are symptoms of bleeding and bruising that you should keep an eye on during cancer treatment. Inform your health care team if you are experiencing any of the below symptoms:
- Bleeding from mouth, nose, or rectum
- Blood in spit or vomit
- Bleeding excessively for even a small injury
- Bruises on the skin from unknown causes
- Heavy bleeding from the vagina during menstrual periods
- Red or purple coloured dots on your skin without any injury
- Brown, pink, or red coloured urine
- Weakness
- Blood in stools making the stool black and tarry
Deeper bleeding can result in;
- Dizziness, confusion, or very sleepy
- Severe headache
- Joint or muscle pain
- Vision changes like blurred vision, double vision, etc
How Bleeding And Bruising Can Be Treated?
There are some possible ways to treat bleeding and bruising or thrombocytopenia by your cancer care team;
- If your platelet count is low but you require surgery to treat cancer, you should wait until your platelet count grows to normal. This will reduce the risk of heavy bleeding during or after surgery.
- If you experience bleeding and bruising as a side effect of cancer treatments, then your doctor may change treatment plans. This includes changing treatments, medications, or doses that could affect platelet count.
- In some cases, your doctor may order a transfusion of platelet cells where you receive blood from a donor through infusion. This will treat heavy bleeding temporarily.
- Your doctor can also prescribe drugs that stimulate the bone marrow to produce more platelets.
Ex. Oprelvekin – Available as Neumega, is a blood cell growth factor approved by the FDA for the production of platelets in the body.
- Vitamin K can be used to prevent bleeding in some patients. It can be given either orally, subcutaneously, or intravenously.
- It can also be treated locally with dressings, packings, topical agents, and by applying pressure.
- Palliative radiation therapy is an effective choice to stop bleeding from cancers. It is commonly used to treat bleeding from skin cancer, lung cancer, cervical, and uterine cancers.
How To Prevent Bleeding And Bruising?
Follow these ways to prevent bleeding and bruising;
- Avoid physical activities that could lead to injuries such as contact sports.
- Protect your skin from scrapes and sharp objects.
- Use lotion or lip balm to prevent bleeding from dry, chapped skin and lips.
- Use a soft toothbrush to avoid bleeding from the gums or mouth.
- Replace the razor with an electric shaver.
- Avoid medicines that increase the risk of bleeding and bruising.
- Ask your dentist or treating team if you can go for floss.
- Don’t blow your nose forcefully. If your nose bleeds, sit up facing your head forward. You can place ice on your nose and pinch your nostrils shut for a few minutes to help reduce bleeding.
- Don’t strain during a bowel movement. If you are suffering from constipation let your treating team know.
- Avoid inserting enemas or suppositories into your rectum.
- Use a soft and clean cloth to gently press the bleeding area. Keep pressing until the bleeding stops. If you bruise, put ice on the affected area.
- Wear shoes to avoid chances of a cut or scrape on your foot.
- Carefully use sharp objects like knives, scissors, needles, etc.
- Avoid or limit alcohol consumption.
The treatments and preventive measures may vary based on the type and site of bleeding or bruising. Don’t forget to contact your health care team if you bleed or bruise more than usual and seek immediate medical attention.
When To Contact Your Doctor?
Contact your doctor right away if you;
- Get large bruises or many smaller bruises from unknown causes.
- Face any signs of infection such as fever, redness around the bruise, etc.
- Bleeding persists or worsens
- Bruises that are painful and don’t go away
- Notice bruising right after taking a medicine
Questions To Ask Your Doctor About Bleeding And Bruising:
Prepare yourself before your visit with the doctor by making notes of all questions you get during treatment. You can add the below questions on bleeding and bruising to your list;
- What could be the cause of my condition?
- What medicines, vitamins, or herbs should I have to avoid?
- Do I have to limit or avoid activities that increase my risk of bleeding like playing, consuming alcohol, or sexual activities?
- What steps should I have to take to prevent bleeding and bruising?
- How long should I have to wait for the bleeding to stop before I call you?
- How to grow my platelet count? Are there any natural ways to increase my platelet count?
- Are there any risks from my current condition?
- What serious symptoms should I have to watch for?
- Does bleeding and bruising show any effects on my cancer treatment?