Dr Shikhar Kumar is a Consultant Medical Oncologist at Onco Cancer Centres, Hyderabad.
Lymphomas are a group of cancers that arise from the cells that reside in our lymphatic system. They are broadly categorized into two types: Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (HL) and Non Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL).
Over the past 50 years, huge progress has been made toward our understanding of the biology and treatment options for HL and NHL.
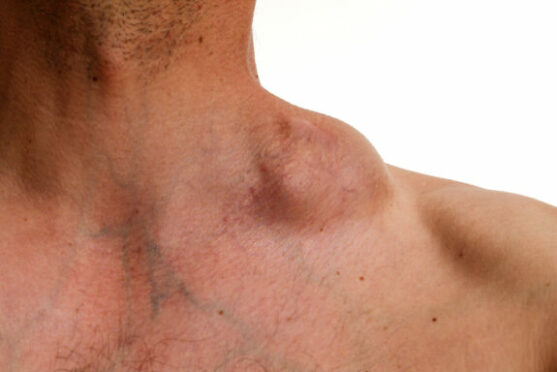
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is an uncommon cancer and accounts for 10% of all lymphomas, with approximately 80000 new cases being diagnosed worldwide in 2018. It occurs predominantly in young adults (20-34 years). The Epstein-Barr virus is implicated in the pathogenesis of this lymphoma. Patients often present with a painless, rubbery, enlarged lymph node mass in the neck, under the armpit or in their groin. They also have symptoms like persistent low grade fever, night sweats and weight loss. Many patients in our country are often mis-diagnosed as tuberculosis and waste several months taking anti-tuberculosis medications and are later diagnosed as Hodgkin’s lymphoma !
The diagnosis of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is confirmed with an excision biopsy of the enlarged node. A PET-CT scan is then done to confirm the stage of the disease. Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a highly curable malignancy, with cure rates of >95% for stage I/II disease and >85% for stage III/IV disease. The chemotherapy regimens include ABVD / BEACOPP , which are given intravenously under the supervision of a medical oncologist. This treatment lasts for a few months. A PET-CT scan is done after 2 cycles, to assess the response and tailor the subsequent treatment accordingly. Some patients are also given radiation therapy at the end of chemotherapy treatment.

Non-hodgkin Lymphoma is a group of more than 30 types of lymphomas, which are again broadly classified into 2 types- “B-cell lymphoma” and “T-cell lymphoma”. The most common subtypes of NHL are called DLBCL (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma) and FL (Follicular Lymphoma). They occur mostly in the 6th and 7th decade of life. DLBCL is a fast growing lymphoma and patients present with a short duration of symptoms and rapidly progressing disease whereas FL is slow growing. The chemotherapy regimen for DLBCL is called R-CHOP which is given every 3 weeks for 6 cycles. The cure rate for DLBCL (which often presents with stage III/IV disease) is approximately 60-70%. FL is treated only when the nodes are large in size and cause discomfort to the patient, and the chemotherapy regimen of choice is called Bendamustine+Rituximab. It is given every 4 weeks for 6 cycles. With this , 70% patients can expect to be free of their disease for upto 5 years.
The backbone of a successful treatment of a lymphoma depends on the pathologist (to give the accurate diagnosis on the biopsy) and the medical oncologist (who administers the most appropriate chemotherapy as per the subtype of the lymphoma and also manages all the side effects). Being a curable malignancy, it is vital that the chemotherapy doses are correct and any delays in treatment are minimized.

