Cancer patients & their families often lament on how unprepared they are after receiving news of their diagnosis.
Keeping this in mind, our team of oncologists has prepared a guide that helps you navigate through your cancer. This is by no means exhaustive, but we hope you find it useful as you begin your treatment journey.
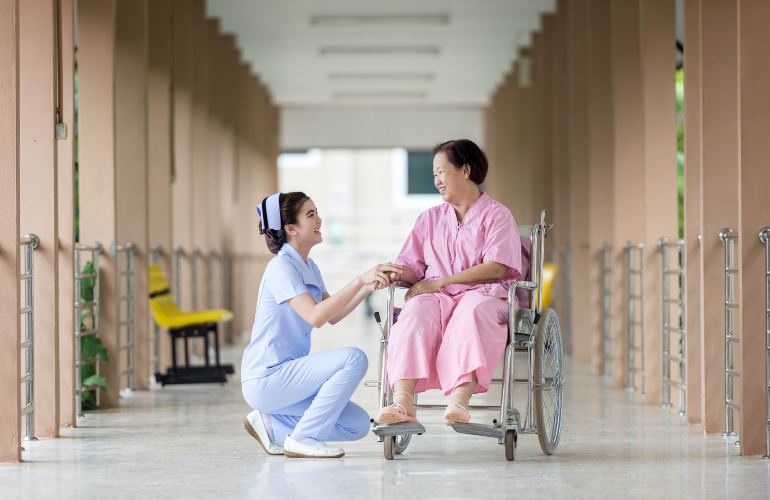



What is Cancer?
Cancer is caused when some abnormal cells of the body start growing in numbers uncontrollably, and overcrowd the healthy cells, thereby affecting the functioning of body organs.
Cancer can sometimes stay hidden for a long time (as seen in cases of pancreatic cancer) or be detected early on, either because of regular cancer screening/health-check-ups or through unusual symptoms experienced by the patient.
Symptoms Seen Commonly In Cancer Patients
Please note that symptoms may differ, depending on the site, type and size of cancer. The most common symptoms of cancer are listed below:
- C: Change in bowel or bladder habits
- A: A painless oral/skin sore that does not heal
- U: Unusual bleeding or discharge from the Nipple, Vagina, in urine or in stools
- T: Thickening or lump in the breast or elsewhere
- I: Indigestion or difficulty in swallowing
- O: Obvious change in a wart or mole
- N: Nagging cough or hoarseness of voice
Also notable is that these symptoms are not necessarily indicative of cancer; neither are they comprehensive. It is best to talk to your doctor/general physician if/when you experience any unusual symptoms.




How Is Cancer Detected?
The following tests help in the detection of cancer and the determination of its stage:
- Lab Tests: Typically, blood and urine tests are performed to detect a few common cancer types. These also help in detecting recurrences in some cases, through tumour marker studies.
- MRI Scans: These scans reveal a detailed internal image of body tissues.
- Ultrasound Tests: These provide an image of an internal part of the body through echoed sound waves.
- X-rays: X-rays are sometimes the first tests done to detect any bony abnormality. Chest X-rays also help in detecting if cancer has spread to the lungs.
- PET-CT Scans: These tests help detect cancerous areas as glowing hotspots in any part of the body. Such spots are then tested with a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer. These also help in confirming whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Biopsies: In a biopsy, a small piece of lump is extracted from the cancerous area, and checked for the presence of cancer cells. A biopsy is often a confirmatory test to diagnose cancer.
Once a biopsy report confirms cancer, a diagnosis is made.
What A Cancer Diagnosis Reveals
- Type Of Cancer: This is dependent on the body organ where the cancer first originated.
- Grade Of Cancer: Grade helps in predicting how fast the cancer will grow and spread. Higher-grade cancer grows fast and often requires aggressive treatment protocols.
- Stage Of Cancer: Cancer stage can be 0,1,2,3 or 4. A 4th stage cancer implies that a cancer has spread wide from its site of origin.
- Metastatis (Y/N): Cancer is termed metastatic once it has spread to other body parts. For example: a lung cancer can spread to the brain, etc.
Cancer Treatment Options
Cancer treatment options are comprised of one or more of the following:
- Surgery: A surgery is often performed to remove the tumor from a body part. It is most effective when the cancer is localized (early stage) and non-metastatic.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation treatment involves killing of cancer cells by subjecting the tumour to X-ray radiation. It can either be from external or internal sources.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the administration of drugs to kill cancer. These drugs are very toxic in nature and sometimes attack healthy cells as well. Therefore, patients on chemo drugs often experience severe side effects.
- Targeted Drugs: Targeted therapies only affect the cancerous cells in the body and exclude all healthy cells from their effects. Therefore, they have less severe side effects as compared to chemo drugs. There are several targeted therapies available in the market today, for certain types of cancers.
- Immunotherapy: This is a cutting-edge treatment option in cancer care today, and it involves training the immune system of the body to attack cancer cells.
- Other Advanced Therapies: The field of cancer research has seen major clinical advancements in the last decade. Hundreds of cutting-edge therapies are in development presently, and will be approved in the coming years. It is worthwhile to check if there are any clinical trials recruiting near you for these therapies.
Do you have a specific question about cancer that you want our team to answer on this blog? Write to us at team@onco.com.





