Biopsies are crucial diagnostic aids in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Most cancers are diagnosed and staged based on the biopsy results, and even many treatment types are decided based on these results.
However, there are many misconceptions and myths regarding biopsy that may prevent the patients from availing the benefits of this procedure; hence there is an urgent need to dispel these false notions surrounding biopsies.
About Biopsy
Biopsy is a minor surgical procedure that involves collection of a sample of cells or tissue from the affected body and examining them under the microscope to check for the presence of cancer. The procedure can also be performed to determine the treatment response.

biopsy needle
It is usually recommended when something suspicious is noticed during a physical examination or other tests, or if the symptoms of the patient indicate a likelihood of a cancerous growth. Apart from cancer studies, biopsies can also help determine several other conditions, such as infection, inflammatory condition, or any autoimmune disorder.
There are many types of biopsies, based on their purpose and the method of doing it. The common ones include incisional and excisional, needle biopsy, scalpel biopsy, and liquid biopsy.
Myths and Facts About Biopsies
With the advances in medical technology, the number of biopsies has increased and are performed largely by radiologists or surgeons. Although it is the gold standard for diagnosing more than 90% cases, patients may still be sceptical about undergoing a biopsy, due to the many myths associated with the procedure.
-
Myth: Biopsy is a dangerous operation
Fact: Generally, all the surgeries and medications carry some risk, the only difference is how much damage this procedure would cause. It is always good to weigh the risks against the benefits, and for biopsies in most patients, the benefits outweigh the risks involved.
Biopsy is not a dangerous operation, but like all surgeries it does have risks, although very minor. Biopsies rarely cause bleeding, infections, and scarring. However, these risks are based on the location of tissue collection, biopsy type and other comorbid conditions the patient is suffering from.
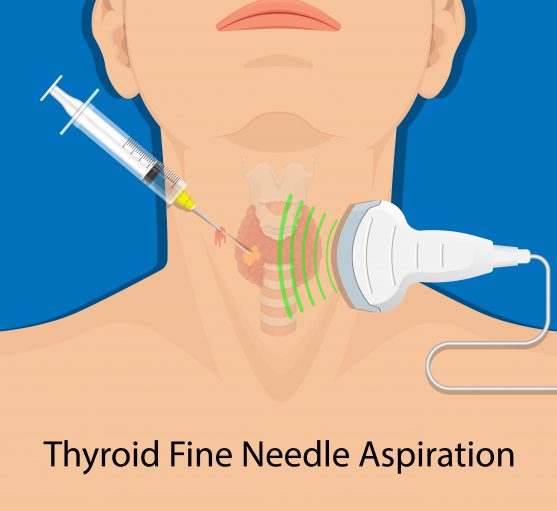
-
Myth: Biopsy causes the cancer to spread
Fact: For many years, patients and even some physicians believed that cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body following a biopsy. However, there is not enough appropriate scientific evidence to support this notion. While there are a few case reports, which suggested that this might occur in rare cases. This possibility can be effectively avoided by taking all the necessary steps to prevent the spread of cancer cells during the sample collection.
To dispel this belief a study was performed by researchers at Mayo Clinic’s campus in Jacksonville, Florida. The study concluded that patients who had undergone biopsy had better outcomes and longer survival rates when compared to the patients who refused to have a biopsy.
-
Myth: Biopsy can increase the stage of cancer
Fact: There is no conclusive evidence that a needle biopsy will increase the stage of cancer. Theoretically, during biopsy needle withdrawal the tumour cells may migrate into the surrounding skin and soft tissue through the biopsy needle. However, practically, this occurrence is very rare and has very little impact on the patient’s treatment outcome.
Biopsy may benefit the patient in several ways by making accurate staging and relevant treatment planning possible. Patients who anxiously inquire about the risks and complications of this procedure, can be reassured that, even if this occurs, the clinical effect is negligible, and the rate of disease recurrence is very rare. The benefits far outweigh the risks.
-
Myth: Biopsy is not necessary for cancer treatment
Fact: Biopsy confirmation is necessary before contemplating treatment in more than 90% of cancers.
A postoperative surgical biopsy can offer clues about the stage and extent of the cancer, which plays a key role in the cancer treatment plan and also response to treatment done. Especially in metastatic cases, biopsy samples are further subjected to molecular studies to see the role of any advanced therapies like targeted therapy, immunotherapy.

Preparing samples for diagnosis
Targeted therapy is an effective treatment option for cancers. This therapy uses drugs or other substances to precisely target specific genes and proteins involved in the cancer growth and development. Here, a biopsy plays a crucial role in identifying the specific molecules to target.
Additionally, some types of biopsies, such as liquid biopsy can be used to assess the response of tumour to the treatment, provide early information about cancer recurrence, and determine the reasons for treatment resistance.

Examining the sample under a microscope
-
Myth: Biopsy always needs hospitalisation
Fact: Most biopsies are minor procedures and require local anaesthesia, hence can be performed as an outpatient procedure.
However, some biopsies that involve collecting a tissue sample from the internal organs, such as liver or kidney, may need to be performed under general anaesthesia. In such cases, the patient might require an overnight stay in the hospital to recover from the effects of anesthesia.
Verbal, written or casual exchange of information is common in any healthcare setting; unfortunately, false notes are heard too soon and are spread easily. The only way to overcome these myths is to encourage the patients to talk about their concerns with the healthcare team who can provide them the correct and unbiased information based on strong scientific evidence.
The healthcare professionals also need to take initiatives to promote patient education and counselling services in their healthcare set-ups.



