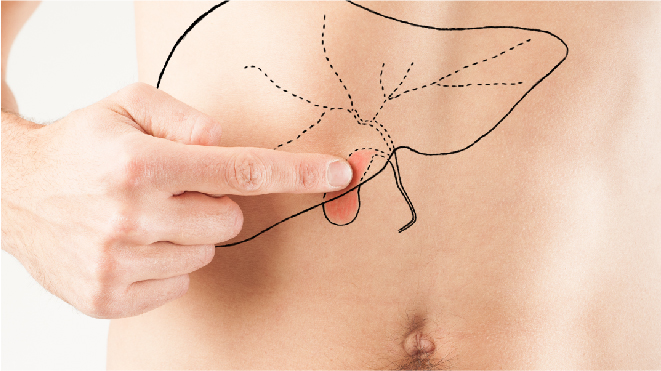
Gallbladder cancer as the name suggests, begins in the gallbladder, an organ that stores a substance called bile. To read about gallbladder and gallbladder cancer, click here
Surgery for gallbladder cancer:
Surgical procedures for treating gallbladder cancer can be broadly categorized into two types: potentially curative surgery and palliative surgery. Potentially curative surgeries are for resectable cancers, that is for the cancers which can be completely removed by the surgical procedures while, palliative surgeries are used for metastasized cancers for which surgical methods alone cannot eliminate the cancer from the body. Read more about surgery for gallbladder cancer here
Complications for gallbladder cancer surgery:
Surgeries are often very complex procedures and can have major side effects on the patient. In treating gallbladder cancer, surgeries include resection of the gallbladder along with the surrounding organs depending on the spreading of the cancer. Hence, a lot of complications arise post surgery.
The complications vary from individual to individual. The patient must be in constant observation during and after the surgery. A few of these last for a few days post the treatment, but the patients have to deal with a few for their lifetime. The following are some of the complications that arise post surgery of gallbladder cancer:
Short term complications:
The following are the short term complications after surgery in gallbladder cancer:
Nausea and vomiting:
When surgery is done to remove the gallbladder, the effect of the treatment is also on the surrounding organs like the stomach and the intestines. This causes disturbances in the digestion which might lead to vomiting and weakness.
Abnormalities in blood cell count:
A lot of blood is lost during and after the treatment. This might lead to a reduced blood cell which can cause the following:
- Anemia: Lowered red blood cells cause severe weakness in the body.
- Infections: Low white blood cell count makes the patient prone to infections.
- Bleeding: Lowered platelet count can cause difficulties in blood clotting and excessive bleeding.
Problems with eating and drinking:
Surgical removal of the gallbladder involves the removal of portions of the surrounding organs which are responsible for the digestion of food. This results in the patients experiencing discomfort in the stomach, heartburns and changes in their regular diet.
Pain:
The resection of gallbladder is carried out making incisions on the abdomen. This causes a lot of pain post treatment, during the healing.
Anesthetic problems:
People who are sensitive cannot take higher doses of anesthesia as they can have reactions in the body after the procedure.
Long term complications:
The following are the long term complications of surgery for gallbladder cancer:
Diarrhoea:
The removal of the gallbladder results in the bile flowing directly into the small intestine, which is why stools stay for lesser time in the bowels. Surgical procedures that are used for treating gallbladder cancer can affect the bowel movements. Almost 20% to 30% of the patients experience diarrhoea post the removal of gallbladder. Diarrhea is an immediate side effect of surgery for the gallbladder. It might even continue for a few years. Antidiarrheal drugs and changes in diet plan can help in slowing down the bowel movements.
Post-cholecystectomy syndrome (PCS):
This happens post gallbladder removal as it alters the flow of bile. It can start immediately after the treatment or while later. Symptoms of this syndrome include heartburns, indigestion, constant pain of abdomen, diarrhea, bloating, fever or jaundice.
Bile duct injury:
During the removal of gallbladder, there could be a damage to the bile duct. This leads to leakage of the bile and abdominal pain post the treatment. It often occurs after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surgery is sometimes required to repair this leak, by placing a stent in the damaged duct.
Digestion problems:
The radical resection of the gallbladder affects the pancreas also. This damage can lead to an inability of the pancreas to efficiently secrete the digestive enzymes, which causes trouble in digestion. Patients are often advised to externally take digestive enzymes which help in better and fast digestion of food.
Diabetes:
After the removal of gallbladder, the patients are at a very high risk of developing diabetes. This problem will worsen if the patients have blood sugar problems in the past.
Liver damage:
As a part of surgery for advanced gallbladder cancer, a portion of the liver is also removed or the functioning of the liver is affected. This might lead to a liver failure in a few patients.
After treatment:
Post treatment care is very important for any disease or treatment, even more so for conditions that can be terminal or have major side effects. Read more about the treatment outcome and post treatment care for gallbladder cancer here