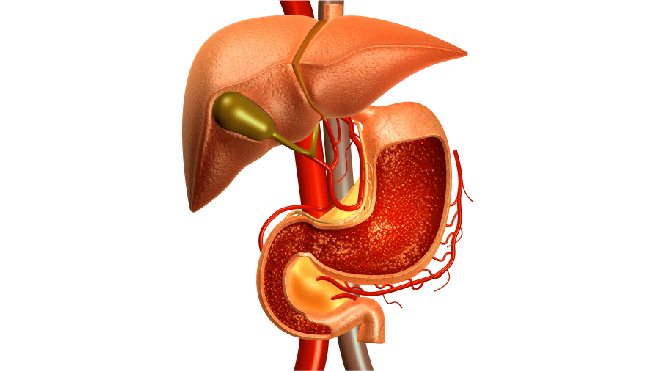
Cancer begins when there is abnormal growth and division of the cells in any part of the body and the cancer that develops in the gallbladder is known as gallbladder cancer. The gallbladder which is located on the right side of the abdomen, behind the liver and is responsible for the storage of bile. To read more about the gallbladder and gallbladder cancer, click here. This is a very rare cancer and is one of the most treatable forms when diagnosed in the early stages. But most gallbladder cancers are diagnosed in the advanced stages which affects its survival rate.
What are the causes of gallbladder cancer?
Gallbladder cancer is caused due to the mutations in the DNA of the cells in the gallbladder. These mutations lead to division and abnormal growth of the cells. These extra cells form tumours that spreads to other organs. The exact cause of the cancer varies from each person. Gallbladder cancer can be caused due to a lot of risk factors, however the exact causes of the cancer are still being researched.
Risk factors of gallbladder cancer:
When the exact causes of a disease are not known, certain factors that are involved with it are noted and these are called the risk factors. The risk factors are the conditions that suggest higher probabilities for developing a certain disease, in this case gallbladder cancers. Presence of risk factors does not imply that a person will get cancer but only indicates likelihood. Same is true with the converse, a person can get gallbladder cancer even in the absence of all the risk factors. Some risk factors for gallbladder cancer are as follows:
Age:
The age of the patient is one most common risk factors for gallbladder cancer. It is often observed in people over 70 years and rarely in people younger than 50 years.
Sex:
Gallbladder is more common in women than men. For every 10 cases of gallbladder cancer, 7 are women.
Cholecystitis and gallbladder cancer:
The existence of gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder known as cholecystitis is a major risk factor of gallbladder cancer. Almost 80% of the patients with gallbladder cancer have gallstones. The gallstones are formed due to depositions of cholesterol and bile minerals.
Family history:
People whose predecessors have gallstones are more prone to develop gallbladder cancer. BRCA2, a genetic mutation also increases the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Smoking and exposure to chemicals:
People who smoke are more likely to develop gallbladder cancer. Also, exposure to chemicals like nitrosamines causes the mutations in the DNA. Workers in rubber and metal industries are usually exposed to these chemicals.
Porcelain gallbladder:
This occurs when calcium deposits on the inner wall of the gallbladder as a cause of repeated cholecystitis and this condition can lead to gallbladder cancer in a few patients.
Primary sclerosing cholangitis:
The inflammation of the bile duct also increases the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Defects of the pancreas and bile ducts:
Abnormal attachment between the bile duct and the pancreas and the outgrowths in the bile duct raise the risk of patients developing gallbladder cancer. These defects of the pancreas and bile ducts are formed during the birth itself, but they show up in the later ages.
Gallbladder polyps:
These are non-malignant growths in the gallbladder and in time, these can develop into cancers.
Obesity and diet:
Overweight or obesity leads to hormonal changes in the body that caused repeated cholecystitis, which increases the risk of developing gallbladder cancer. Foods low in fibre and high in carbohydrates contribute in raising the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Diabetes
People with high diabetes are more prone to develop gallbladder cancers.
Hormone replacement therapy
Hormone transfusion or replacements raise the risk of the person developing gallbladder cancer. Women who are exposed to high levels of oestrogen during these therapies are more inclined to develop the cancer.
Salmonella infection
Patients who have gallstones are at a higher risk of developing gallbladder cancer due to typhoid causing salmonella infection.
Prevention of gallbladder cancer:
There are no specific ways to prevent gallbladder cancer only avoid the risk factors, though early detection significantly increases the survival chances of the patient. To read about the signs and symptoms of gallbladder cancer, click here. Following are the tips to reduce the risk of developing gallbladder cancer:
Reduce weight
The patients are advised to gradually reduce weight. This helps them prevent gallstones. Also, since obesity is a major risk factor of gallbladder cancer, reducing weight will minimize the risk. Regular exercising will help patients reduce weight and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Diet
Following a healthy diet and not pressurizing the liver much will help in minimizing the risk of developing gallbladder cancer. Following are the do’s and don’ts to maintain a healthy diet:
- Reduce foods that are high in carbohydrates
- Have foods that are rich in healthy fats
- Consume high fibre foods
- Avoid sugars
Protecting your liver
The liver is responsible for the detoxification of the food that is consumed by the person. In case the liver is over pressurized or does not function properly, there is a high risk of damage to the gallbladder, which can cause gallbladder cancer.
Surgery
Surgical removal of gallstones is often recommended to patients before they lead to gallbladder cancer. To read about surgical procedures available for gallbladder treatments, click here