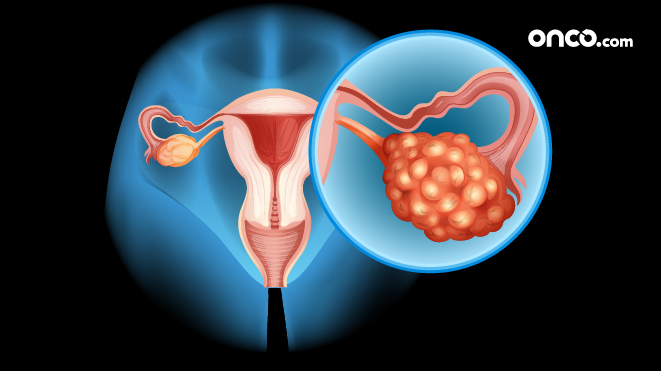
What are the different types of ovarian cancer?
World Health Organisation (WHO) and International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) adopted a single classification of the common epithelial, germ cell, sex cord, and stromal tumours. 60 to 65 % of ovarian cancers are epithelial tumors, around 20% are germ cell tumors.


Epithelial cells
These cells are found on the outer surface of the ovary and studies have linked these cells to epithelial cell tumors.
Germ cells
Ovarian germ cells are known to be the surface cells of the adult ovary that represent the germ line. These are also known as competent embryonic stem cells. They are linked to ovarian germ cell tumors.
Stroma cells
The stromal cells of the ovary are spindle shaped and appear to be similar to that of fibroblasts. However, ovarian stroma differs from the typical connective tissue and is distributed in such a way that it appears whorled. The stromal cells are associated with maturing follicles that exhibit endocrine function as well as the function of secreting estrogen.
Aside from these cellular associations, there are a few other situations where malignant or cancerous tumors can develop inside the ovaries and spread to other nearby organs or tissue areas.
Epithelial ovarian tumors
Epithelial ovarian cancers arise from epithelium covering the ovary. There are four main subtypes of epithelial tumors. they are serous, endometrioid, mucinous, and clear cell.
Borderline epithelial tumors
These tumors were also previously known as low-potential malignant tumors. they are a variety of epithelial tumors. They are less aggressive and has favourable outcome. These tumors are known to be different from the usual types of ovarian cancer tumors, since they don’t grow into the supporting tissue of the ovaries (which is also known as the stroma).
Malignant germ cell tumors
Germ cell tumors are thought to arise from primitive germ cells in the embryonic gonad. The common ones include teratomas, dysgerminomas, endodermal sinus tumors, and choriocarcinomas. These tumors are more common in young women.
Teratomas
Teratomas are germ-cell tumors that contain one or more of three germ layers cells. These three layers consist of the endoderm (which is the innermost layer), the mesoderm (which is the middle layer), and the ectoderm (which is the outermost layer).
Germ cell tumors which are non-cancerous or benign are called mature teratoma and the cancerous forms are called immature teratoma.
Dysgerminoma
Dysgerminoma is a common type of germ cell tumor that usually affects women in their twenties. Around 10 to 15% of these tumors occur bilaterally (affect both ovaries). The treatment includes surgery followed by adjuvant therapy in the form of chemotherapy or radiation.
Endodermal sinus tumor and choriocarcinoma
These are very rare tumors that grow and spread rapidly but are usually very sensitive to chemotherapy. Choriocarcinoma is a tumor that usually originates in the placenta during pregnancy and is more common than the type of cancer that originates inside the ovary.
Ovarian stromal tumors
These tumors mostly develop in women after they have attained the age of 50, but in a few rare cases, they can also occur in young girls. The most common symptoms of these kinds of tumors are seen to be abnormal vaginal bleeding. This is usually caused because the tumors produce a lot of the female hormone, estrogen. This kind of abnormal bleeding is seen in women after menopause.
The common types of tumors are granulosa cell tumors, granulosa-theca tumors and Sertoli-Leydig tumors, which are usually considered to be low-grade cancers. The two types of benign stromal tumors are thecomas and fibromas.
Small cell carcinoma tumors
Small cell carcinoma tumors of the ovary are a rare and highly form of malignant tumors that mainly affect young women.
