Thyroid cancer starts in the thyroid cancer which is located in the neck below the larynx and is responsible for the production and regulation of hormones in the body. Cancer in thyroid affects that person’s metabolism also. Read more about thyroid cancer here.
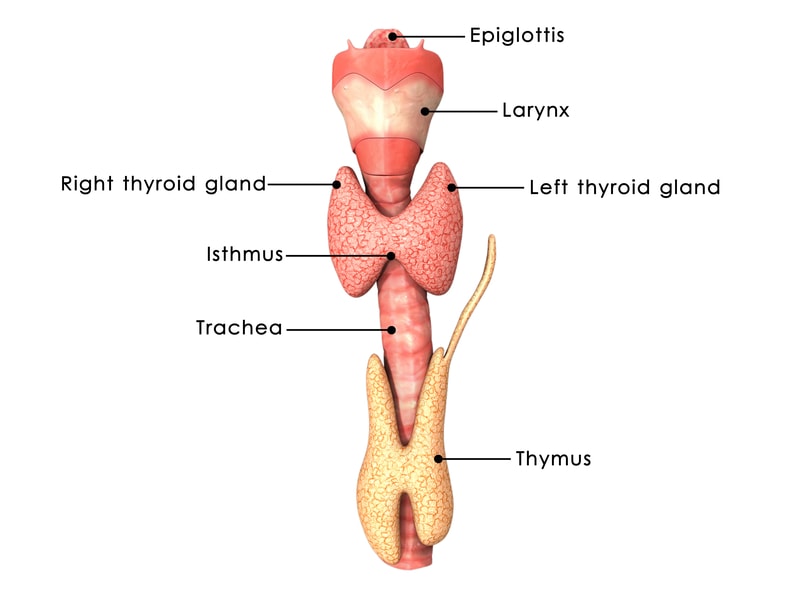 What are thyroid nodules?
What are thyroid nodules?
Tumours in the thyroid are also called thyroid nodules and these are formed due abnormal overgrowth of cells in the thyroid gland. These are very common with at least half of the people having one nodule by the age of 60 years. 95% of the thyroid nodules are benign though and and only 5% are cancerous in nature.
The thyroid glands basically contains two types of cells and the tumours begin in one of these two types:
Follicular cells:
The follicular cells produce the thyroid hormone, which controls the metabolism of a person’s body. Any change in this hormone affects the weight, heartbeat, body temperature, digestion of food, muscle contractions and replacement of dying blood cells.
C cells:
These cells in the thyroid glands are responsible for the production of a hormone called calcitonin. This hormone controls the metabolism of calcium in the body.
What are the types of thyroid cancer?
Following are the 5 types of thyroid cancer:
- Papillary thyroid cancer
- Follicular thyroid cancer
- Hurthle cell cancer
- Medullary thyroid cancer
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer
Papillary thyroid cancer:
This is one the most common and slow growing thyroid cancers which develops from the follicular cells. It is often observed in one lobe, it can occur in both lobes but rarely does. This type of thyroid cancer is a very differentiated one, which means that the tumour is not very different from the normal thyroid tissue when observed under a microscope. This is often metastasized to lymph nodes. The 10 year survival rate of papillary thyroid cancer is above 90%, which makes it a very curable form of cancer.
Treatment:
- Surgery
- Hormone therapy
- Radioiodine therapy
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
Learn more about the treatment options for thyroid cancer here.
Follicular thyroid cancer:
Follicular thyroid cancer is one of the rare types that begins in the follicular cells of the thyroid gland and is a differentiated form of cancer meaning the tumour cells resemble the normal cells. This cancer has a slow growth and does not often spread to the lymph nodes. Only 10% of follicular thyroid cancers are at a risk of spreading to other organs like lungs or bones. However, it is successfully treated with a good prognosis in patients who are below 50 years with a cure rate of 98%.
Treatment:
- Thyroidectomy
- Lobectomy or lymph nodes removal
- Radiation therapy
- Hormone therapy
Hurthle cell cancer:
This cancer is also known as hurthle cell carcinoma or oxyphil cell carcinoma and it develops in a particular type of follicular cells. Accounting for 3% of all types of thyroid cancer, this is a very rare type. These cancers often metastasizes to other lymph nodes. The 5 year survival rate of hurthle cell carcinoma is 45% to 90% while the 10-year survival rate is between 45% and 80%. This success rate completely depends on the patient which increases its unpredictability.
Treatment:
- Radioactive iodine-131 treatment
- Levothyroxine treatment
- External radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Surgery
Medullary thyroid cancer (MTC):
The medullary thyroid cancer is a very metastasizing type of thyroid cancer. It is developed in the C cells of the thyroid gland but can also occur as a result of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN 2). These cancers are also responsible for the production of high doses of calcitonin and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). About 25% cases of MTC are familial. To check if the family members also have MTC (it is called familial medullary thyroid cancer, FMTC), RET proto-oncogene test is done. Read more about the diagnostic tests of thyroid cancer here.
Accounting for 3% of thyroid cancer, this becomes a rare form of cancer. If it is diagnosed and treated before it spreads to other parts of the body, it can be controlled. In almost all of the patients, the cancer is confined to the thyroid gland with a 10 year survival rate of 95.6%. The general 10 year survival rate of all patients treated for MTC is 75% to 85% which makes MTC one of the most treatable forms of cancer.
Treatment:
- Thyroidectomy
- Thyroid hormone therapy
- Radioactive iodine therapy
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Anaplastic thyroid cancer:
This is one of the rarest type of thyroid cancers, accounting for only 1% of all the thyroid cancers. Anaplastic carcinoma has a very fast growth, and hence it spreads to the other parts of the body quickly too. Because of this reason, it is not easy to treat this type of cancer successfully. Anaplastic thyroid cancer has a very low success rate, having a 5 year survival rate of 7%.
Treatment:
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Clinic trials



