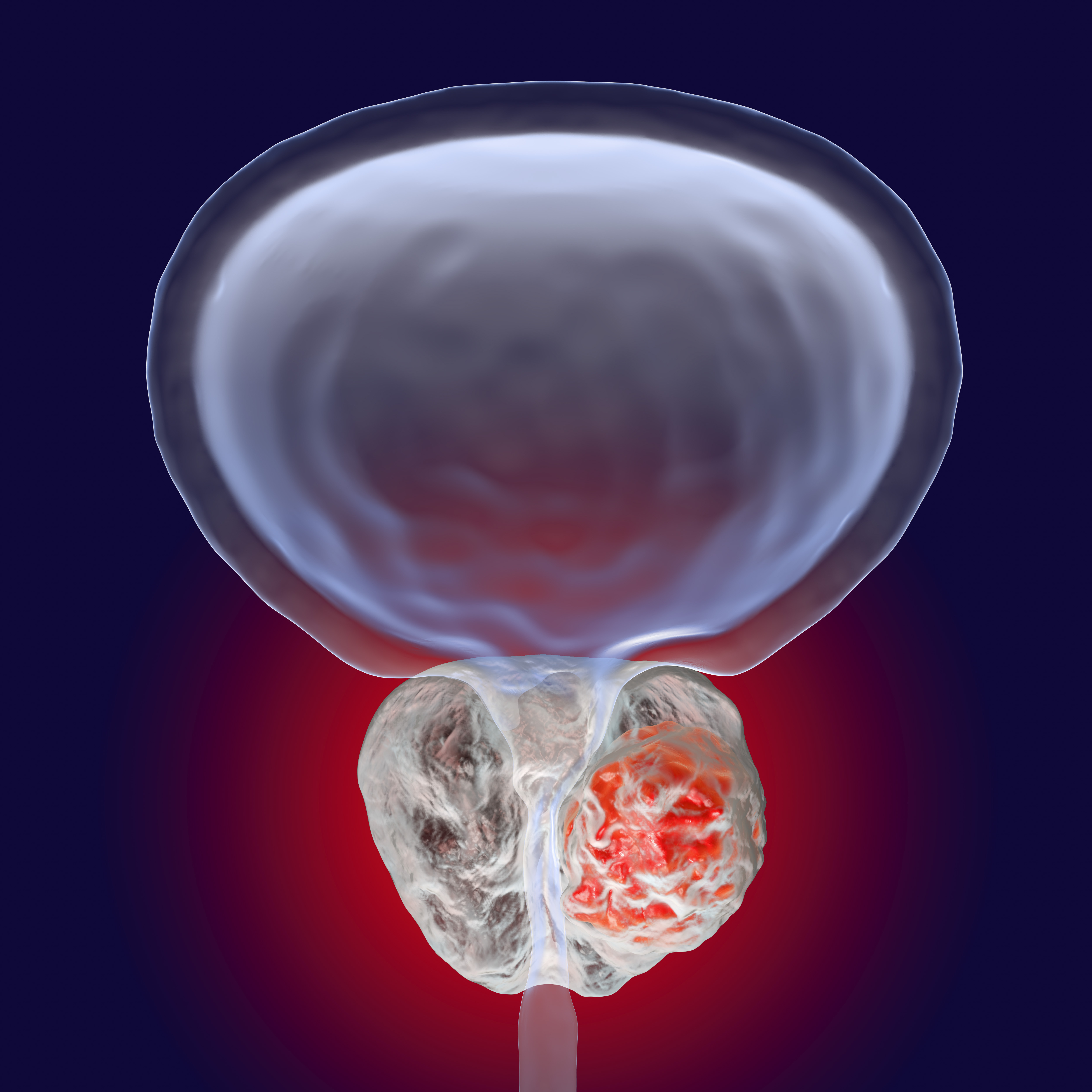
The abnormal growth and division of cells in any part of the body causes cancer. Prostate cancer occurs in the prostate which is an exocrine gland. Read more about prostate cancer here. Prostate cancer does not cause any signs or symptoms in the early stages. This is because of the location and development of the cancer. It does not often press the urethra, which causes abnormalities in urination or any other symptoms until the cancer has metastasized.
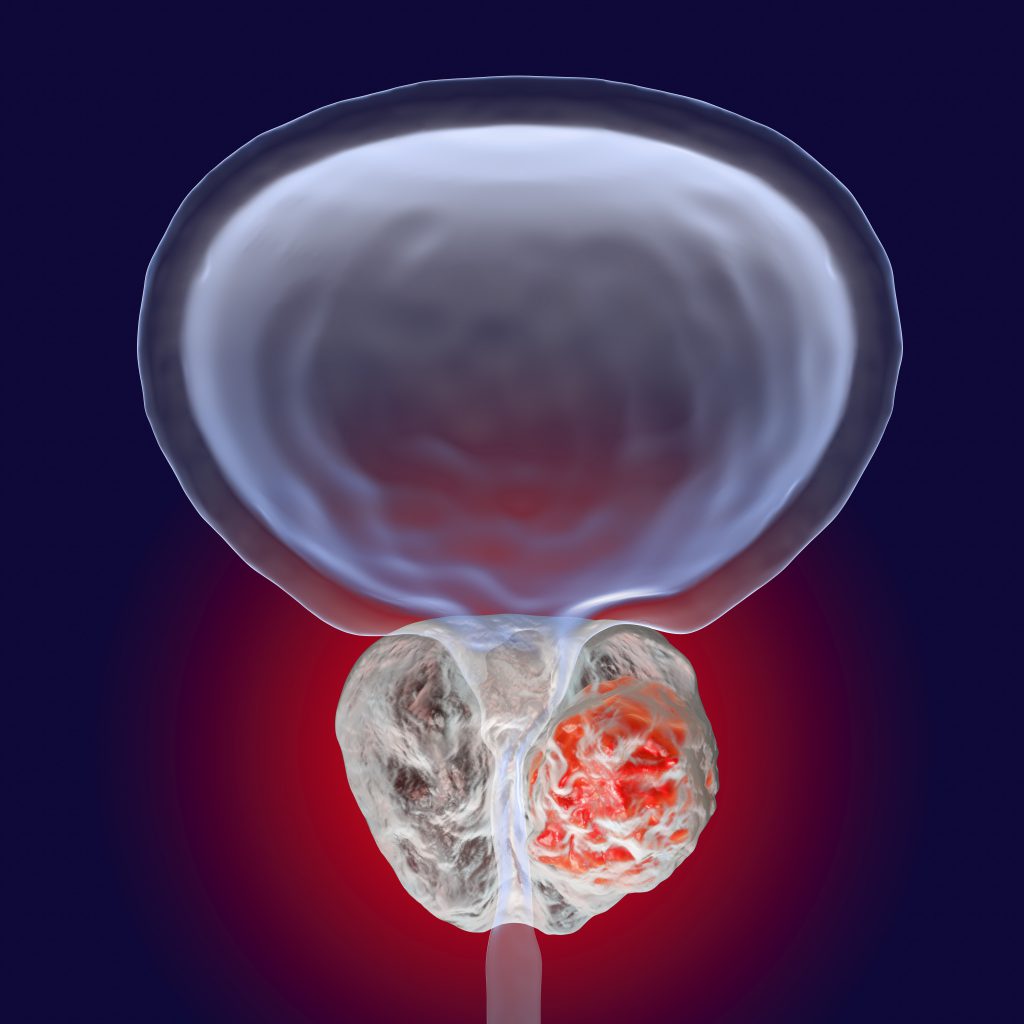
What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?
Most of the symptoms of prostate cancer vary for each individual. The extent of impact of these symptoms on the body depends on the stage of the cancer along with the resistance and tolerance levels of the patient. The common signs of prostate cancer are as follows:
- Reduced control over the bladder
- Blood in urine
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Pain and burning during urination
- Erectile dysfunction
- Swelling
- Bone pain
- Numbness of hips, legs or feet
- Blood in semen
Symptoms of metastasized prostate cancer:
Often, the symptoms show up in advanced stages of cancer. These are complicated and have to be treated particularly. Read more about stages of prostate cancer here.
Following are the symptoms of metastasized prostate cancer:
Fatigue:
Fatigue is a condition of extreme tiredness that lasts even after taking rest. It could be caused due to the development of prostate cancer in the body. It is also caused due to the treatments given to cure prostate cancer, stress or anxiety. Read more on diagnosis of prostate cancer.
Pain:
Not all men experience pain due to prostate cancer. When the cancer has spread to the bones or nerves, it causes pain. It can destroy and weaken the bones, causing bone pain, more like stabbing in men having prostate cancer. The extent of pain depends on the spreading of cancer.
Urinary problems:
If the cancer has spread beyond the prostate into the urethra and the bladder and presses the urethra, men might experience urination problems which include:
- Leaking urine
- Blood in urine
- No control in holding urine in the bladder
- Leaking urine
- No proper filtration of waste from the blood due the blockage of tubes that carry the urine from the kidneys interfering the functionality of the kidneys.
Bowel problems:
Prostate cancer can also cause disturbances in the bowel movement. It causes the following:
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Fecal urgency and inconsistency
- Abdominal pain
- Bowel obstruction
Bone pain and fractures:
Prostate cancer is more commonly spread to the bones. It destroys and weakens them. This type of cancer can cause severe bone thinning which causes extreme damage to the bones leading to fractures.
Sexual problems:
Prostate cancer can reduce a man’s sexual desire. This can be because of the cancer or because of the tiredness caused by it. Advanced stages of prostate cancer can also be a reason of erectile dysfunction in men. Read more on stage 3 of prostate cancer and stage 4 of prostate cancer
Lymphoedema:
It is a condition where the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes which causes a blockage in the lymphatic system which often causes swelling. Lymphoedema in prostate cancer often affects the legs and the pelvic area. Symptoms of this condition in the affected areas are:
- Swelling or inflammation
- Pain
- Discomfort or heaviness
- Skin problems like redness or sore skin
- Infections
Anemia:
Prostate cancer can reduce the blood’s capability of carrying oxygen to meet the body’s needs. This can lead to anemia, a condition of extreme weakness, paleness and shortness of breath.
Metastatic spinal cord compression (MSCC):
This phenomenon occurs when the cancer cells have spread to the spinal cord. The risk of developing MSCC is high when the cancer has spread to the bones. However, this is not often seen in all patients. Following could be the symptoms of MSCC:
- Soreness or pain in the back or neck
- Narrow pain near the abdomen or chest that runs along the lower back, buttocks or legs
- Pain that runs down through the arms or legs
- Weakness causing difficulty in standing or walking
- Permanent numbness and tingling of legs, arms, fingers, toes, buttocks, stomach area or chest
- Reduced control over the bladder or bowel
Hypercalcaemia:
Hypercalcaemia is a condition when there is excessive calcium content in the bones and it begins to leak out into the blood. It is not very common, except for in advanced stages of prostate cancer but might be responsible for the following:
- Bone pain
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Constipation
- Confusion
- Abdominal pain
- Thirsty
- Frequent urination
Eating problems:
Often, men lose their appetite if they have prostate cancer or, are being treated for prostate cancer. This is caused because of the problems they experience in consuming their regular diet, and leads to weight loss.
On experiencing any of the above, a doctor has to be consulted immediately. The patient is then diagnosed based on digital rectal exams (DRE) and prostate specific androgen (PSA) screening tests. Read more about diagnosis of prostate cancer here. If the diagnostic results are positive for prostate cancer, treating the symptoms and relieving the patients from pain is a main part of the treatment, which is known as palliative or supportive care. Read more about treatment options for prostate cancer here.
Also, not all the symptoms cause cancer. They might be a cause of many other non-cancerous conditions like enlarged prostate, urinary infections or other medical conditions.