Breast cancer occurs when cells in the breast tissue mutate and divide rapidly. These abnormal cells form a tumour. A tumour can become cancerous when these abnormally growing cells spread to other parts of the breast or other parts of the body. Metastasis refers to the process by which a secondary malignant growth develops at a new site in the body.. Metastasis happens via the bloodstream or the lymphatic system that helps fight infections.
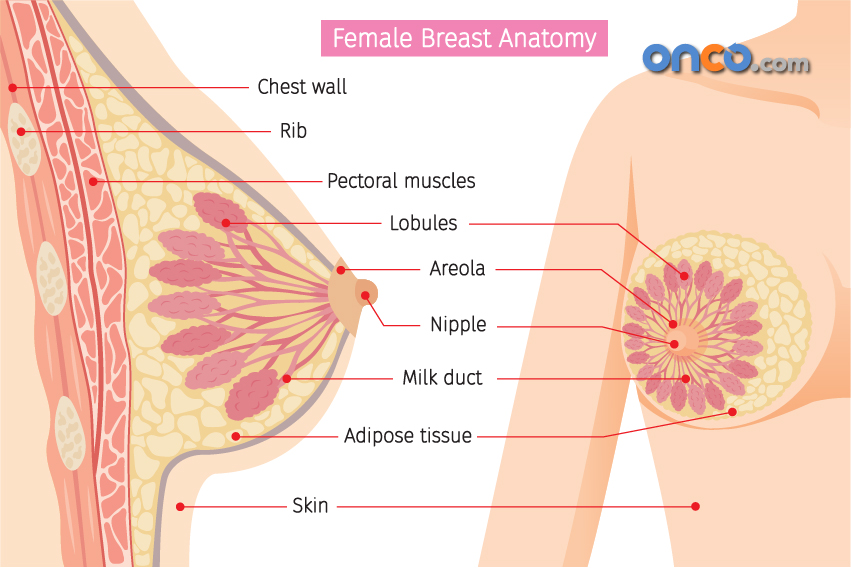
It generally begins in the milk-producing glands (lobules), or in the tube-shaped ducts that carry milk from the lobules to the nipple. Sometimes, it begins taking shape in the fatty and fibrous connective tissue of the breasts.
Both women and men are at risk of developing a tumour in the breast. But it is a hundred times more common in women than in men. It is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in women around the world. But the mortality rates have declined in recent years. Better awareness, regular screening, and advanced treatment options have proved useful.